Criteria to recognize an expert in science and technology for the nuclear sector
Main Article Content
Abstract
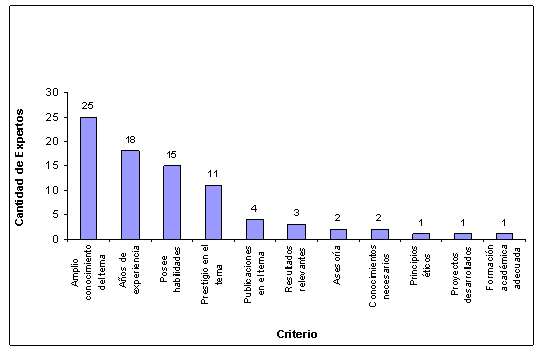
Nowadays, the preservation of knowledge for the future generations is one of the problems in the world because the information is increasing fast as a result of the development of science and technology. In the case of the nuclear activity, the scientific and technological accumulated experiences should be preserved taking into consideration the new applications of the nuclear energy in different sectors of the human activity. For this, it is necessary to know the experts who work on different topics. This paper presents a performed study to obtain criterions from Cuban nuclear professionals about the conditions and principles to take into consideration for the selection of an expert in nuclear sciences and technologies. Appling Delphi method, it was obtained that years of experience, publications, participation in scientific events and scientific degree are more accepted criterions.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
- Los autores/as conservarán sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación esta revista. Bajo esta licencia el autor será libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y crear a partir del material
- El licenciador no puede revocar estas libertades mientras cumpla con los términos de la licencia
Bajo las siguientes condiciones:
- Reconocimiento — Debe reconocer adecuadamente la autoría, proporcionar un enlace a la licencia e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo de cualquier manera razonable, pero no de una manera que sugiera que tiene el apoyo del licenciador o lo recibe por el uso que hace.
- NoComercial — No puede utilizar el material para una finalidad comercial.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales o medidas tecnológicas que legalmente restrinjan realizar aquello que la licencia permite.
- Los autores/as podrán adoptar otros acuerdos de licencia no exclusiva de distribución de la versión de la obra publicada (p. ej.: depositarla en un archivo telemático institucional o publicarla en un volumen monográfico) siempre que se indique la publicación inicial en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as difundir su obra a través de Internet (p. ej.: en archivos telemáticos institucionales o en su página web) antes y durante el proceso de envío, lo cual puede producir intercambios interesantes y aumentar las citas de la obra publicada. (Véase El efecto del acceso abierto).
La Revista Nucleus solo aceptará contribuciones que no hayan sido previamente publicados y/o procesados, por otra publicación. Cualquier violación ese sentido será considerada una falta grave por parte del autor principal lo cual será objeto valoración por parte del Consejo Editorial, el cual dictaminará al respecto.
References
[2]. International Atomic Energy Agency. Managing Nuclear Knowledge (IAEA). Vienna: IAEA, 2003.
[3]. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Comparative Analysis of Methods and tools for nuclear knowledge preservation. Vienna: IAEA, 2011.
[4]. ERICSSON K. Expert performance and deliberate practice. An updated excerpt from Ericsson. 2000. www.psy.fsu.edu/faculty/ericsson/ericsson.exp.perf.html.
[5]. CHACÓN I. Determinación del estado de capacidad de trabajo de instalaciones motrices conservadas [tesis de doctorado]. La Habana: ISPJAE, 2001.
[6]. RUIZ TR. Utilización del método de los expertos (Delfos) para la validación de una estrategia pedagógica. Revista Órbita científica. 2012; 18(69). Disponible en: www.varona.rimed.cu/revista_orbita.
[7]. ELÍAS LL, GONZÁLEZ EV & MARTÍNEZ E. Una propuesta de sistema de indicadores para valorar la formación de expertos en una organización de alta tecnología. Rev. Cub. Inf. Cien. Salud. 2015; 26(1): 20-23. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/pdf/ics/v26n1/rci03115.pdf
[8]. GARCÍA L & FERNÁNDEZ SJ. Procedimiento de aplicación del trabajo creativo en grupo de expertos. Revista Ing. Energética. 2008; 29(2): 46-50. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/3291/329127758006.pdf
[9]. BRAVO ML & ARRIETA JJ. El método Delphi. Su implementación en una estrategia didáctica para la enseñanza de las demostraciones geométricas. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. 2005; 36(7). Disponible en: https://rieoei.org/RIE/article/view/2962/3876.